What this course is all about
This course introduces students to the foundational concepts of AI as they apply to the complex world of robotics, emphasizing how AI algorithms enable robots to interpret sensor data, navigate dynamic environments, and interact intelligently with both objects and humans. The course explores key AI methods, including computer vision, natural language processing, path planning and reinforcement learning that give robots the ability to analyze, reason, and respond to the world around them. Students will engage with hands-on projects with a focus on real-world applications in areas like autonomous vehicles and industrial automation. By the end of the course, students will have gained a deep understanding of how AI enables autonomous robots to perform complex tasks, being instructed with natural language making them capable of working alongside humans in various settings.Topics Covered
Kinematics
Global Planning
Local Planning
VLA Agents
Simulation
Video Lectures
9 modules · 43 lessons · 10+ hours of content
Subscribe to our YouTube channel and explore the complete curriculum below.
1. Course Introduction
1. Course Introduction
2. Statistical Learning Theory
2. Statistical Learning Theory

The Learning Problem
The Vapnik block diagram.

Linear Regression
Extracting non-linear patterns with linear models.

Gradient Descent
Optimizing complicated functions with iterative methods.
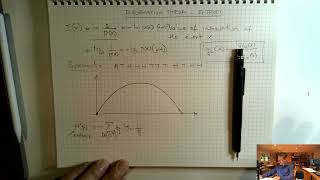
Entropy
Information theory principles.
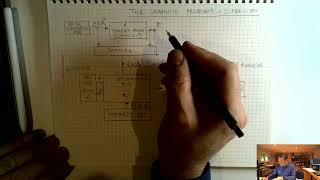
Maximum Likelihood Estimation
The workhorse of statistical modeling.

Binary Classification
Binary classification and Logistic Regression.
3. Neural Networks
3. Neural Networks
4. Convolutional Neural Networks
4. Convolutional Neural Networks
How We Understand Scenes
Human Perception and Imaging.
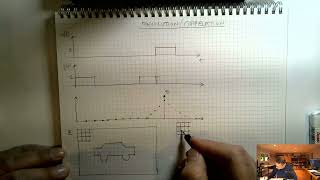
Convolution and Correlation
A linear operation for extracting spatial features.
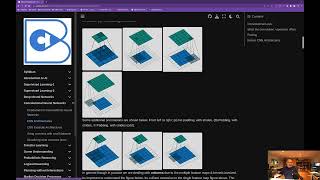
CNN Architectures
Looking inside a CNN layer and understanding architectural patterns.
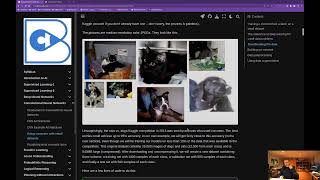
Image Classification
Image classification with data augmentation.
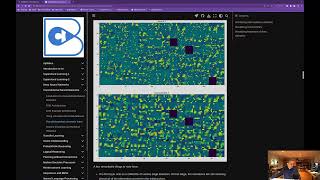
What CNNs Learn
Visualizing the features learned by CNNs.
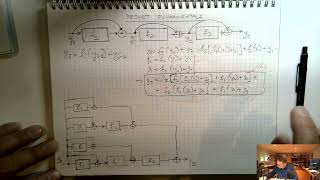
ResNets
Residual Networks and skip connections.
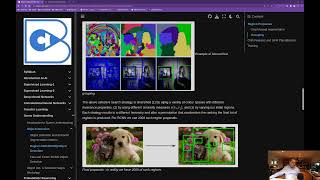
5. Object Detection
5. Object Detection
6. Recursive State Estimation
6. Recursive State Estimation

Introduction to State Estimation with HMM
Introducing Hidden Markov Models.

The Bayes Filter
Implementing the Bayes filter algorithm.
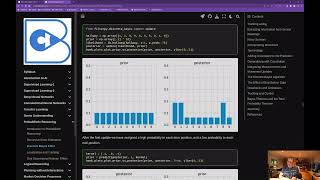
Discrete Bayes Filter Example
Discrete Bayes localization notebook.

Continuous State Space and Kalman Filter
Localizing a drone under Gaussian assumptions.
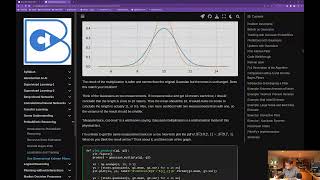
A Kalman Filter Example
Kalman localization notebook.
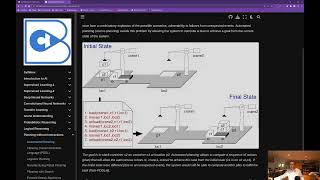
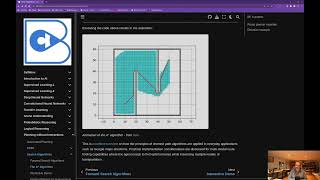
7. Global Planning
7. Global Planning
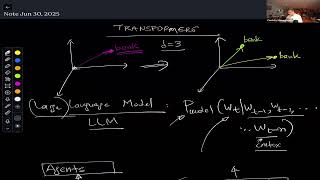
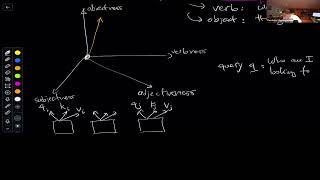
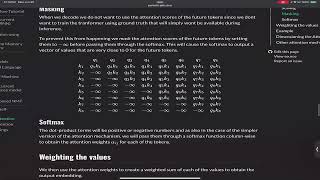
8. Multimodal Reasoning and Transformers
8. Multimodal Reasoning and Transformers
9. Markov Decision Processes
9. Markov Decision Processes

Introduction to MDPs - Part 1
Defining Markov Decision Processes.
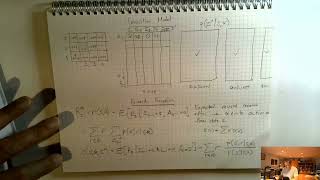
Introduction to MDPs - Part 2
Defining Markov Decision Processes.

Bellman Expectation Equations - Part 1
Deriving the Bellman Expectation Equations.

Bellman Expectation Equations - Part 2
Deriving the Bellman Expectation Equations.
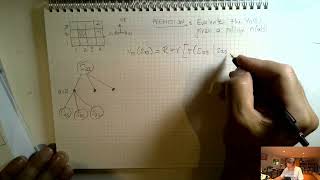
Policy Evaluation - Part 1
Using the Bellman Expectation Equations for Policy Evaluation.

Policy Evaluation - Part 2
Using the Bellman Expectation Equations for Policy Evaluation.
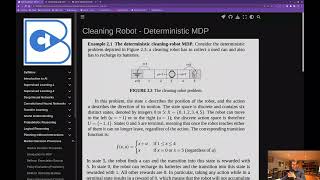
Bellman Optimal Value Functions
Deriving the Bellman Optimality Equations.
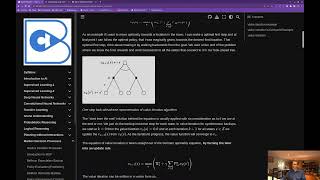
Policy Iteration and Value Iteration
Using the Bellman Optimality Equations for optimal control.